
MedCalc manual: Test for one proportion.(Version 20.109 accessed May 9, 2022) See also Kirkwood BR, Sterne JAC (2003) Essential medical statistics, 2 nd ed.Fleiss JL, Levin B, Paik MC (2003) Statistical methods for rates and proportions, 3 rd ed.
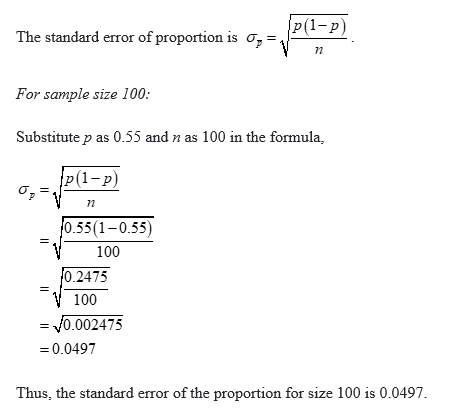
I have two columns (across 400 or so studies) - one that lists numberof patients, and one with the number of outcomes. Hi, I am performing a meta-analysis to identify pooled proportions of patients with specific complications across different subgroups. In the example of the parents with toddlers, the best estimate or the population proportion of parents that uses car seats in all travel with their toddlers is 85. Clopper C, Pearson ES (1934) The use of confidence or fiducial limits illustrated in the case of the binomial. Calculating standard errors of proportions, 09:40. Population proportion or the mean is calculated from the sample.Altman DG (1991) Practical statistics for medical research.MedCalc calculates the "exact" Clopper-Pearson confidence interval for the observed proportion (Clopper & Pearson, 1934 Fleis et al., 2003). If the P-value is less than 0.05, the hypothesis that the observed proportion is equal to the pre-specified proportion value is rejected, and the alternative hypothesis that there is a significant difference between the two proportions can be accepted. The P-value is the area of the normal distribution that falls outside ± z (see Values of the Normal distribution table). Where p is the observed proportion p exp is the Null hypothesis (or expected) proportion and se( p) is the standard error of the expected proportion: The significance level, or P-value, is calculated using a general z-test (Altman, 1991): Null Hypothesis value (%): the pre-specified proportion (the value to compare the observed proportion to), expressed as a percentage.Sample size: the sample size or total number of observations.



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
